Predictive Maintenance: How Modern Manufacturing Prevents Downtime
Machine maintenance is a central pillar of every production environment. It determines how reliably equipment performs, how efficiently workflows run, and how much unplanned downtime a factory must absorb. While traditional maintenance strategies rely on scheduled interventions or reactive repairs, modern industrial environments increasingly adopt predictive maintenance to determine the right moment for service based on real-time machine conditions.
This article explains why maintenance timing is crucial, examines the differences between preventive and predictive strategies, and illustrates how data-driven systems transform production reliability.
Maintenance in Production: Why Timing Matters
Every machine component in a production line is subject to wear, fatigue, and operational stress. Without maintenance, defects accumulate until they lead to failure. The question is not whether maintenance is required, but when it should occur. Maintenance performed too late causes breakdowns, quality issues, and unexpected downtime. Maintenance performed too early wastes resources, interrupts production unnecessarily, and inflates operating costs.
In highly competitive manufacturing environments, downtime—planned or unplanned—directly impacts output, delivery capability, and profit margins. Many companies rely on industry standards and quality frameworks, such as those published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
These frameworks provide guidance for reliability, risk management, and asset health, but timing decisions must still be based on operational realities.
Predictive maintenance addresses exactly this challenge.
Preventive Maintenance: Scheduled but Not Precise

Traditional maintenance strategies generally fall into two categories: preventive maintenance and reactive maintenance.
Preventive Maintenance
Preventive maintenance is performed at fixed intervals—weekly, monthly, or after a predetermined number of operating hours. Manufacturers of machinery often provide recommended service schedules, and companies integrate these intervals into their workflow planning.
Advantages:
-
Provides structure for maintenance teams
-
Reduces likelihood of catastrophic failure
-
Creates predictable plans for spare parts and manpower
However, preventive maintenance also introduces problems:
-
Planning and scheduling are time-intensive
-
Maintenance may be performed too early, wasting time and resources
-
Certain components may fail before the scheduled interval
-
Unnecessary downtime can accumulate because machines are serviced even when no issues are present
Most importantly, scheduled maintenance does not consider actual machine condition. It follows the calendar, not the equipment.
Reactive Maintenance
Reactive maintenance occurs only after a failure has happened. While simple in concept, it is the most disruptive approach:
-
Breakdowns halt production immediately
-
Repair time is unpredictable
-
Damage may spread to other components
-
Emergency labor and express parts deliveries raise costs
Both preventive and reactive maintenance strategies share one major flaw: they lack precise timing.
Neither approach answers the essential question: What is the exact moment a component requires intervention?
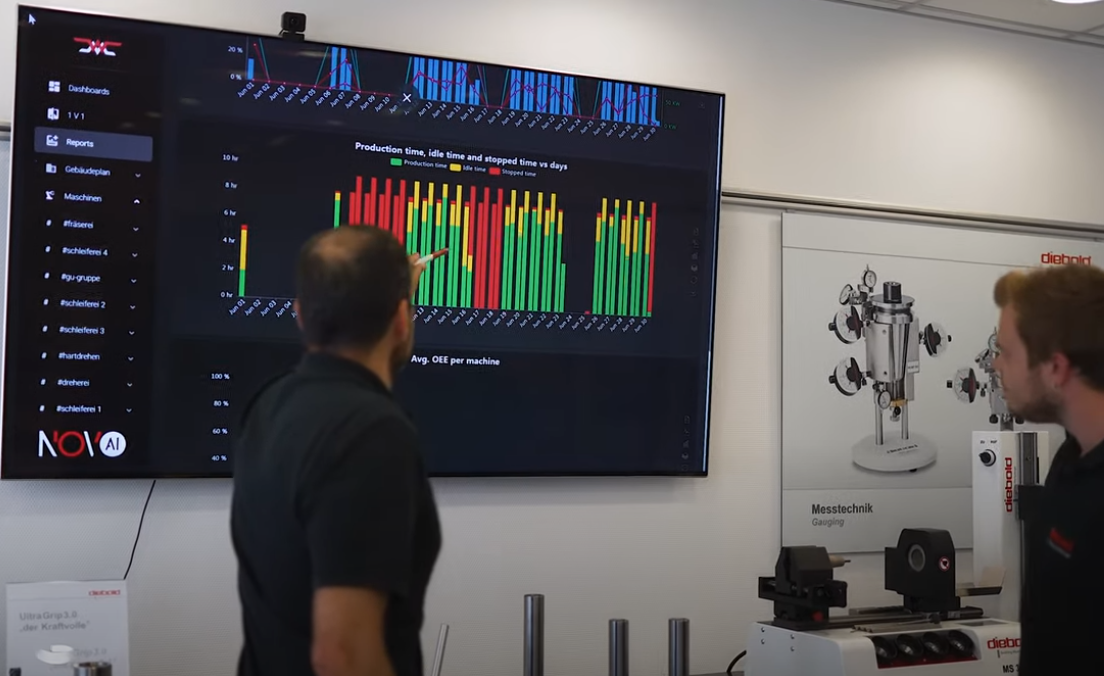
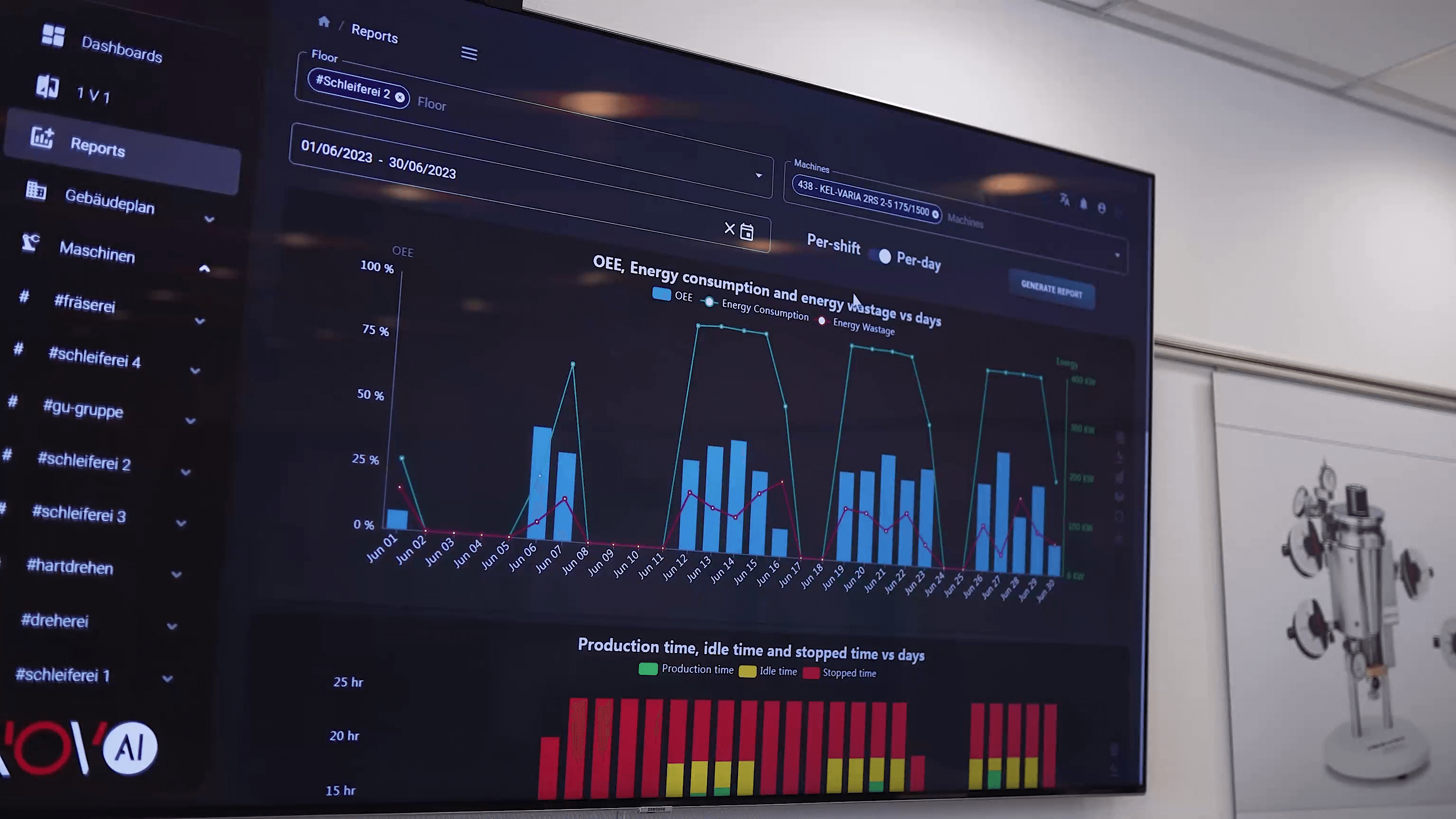
Predictive Maintenance: Data Defines the Moment
Predictive maintenance offers a fundamentally different approach. Instead of scheduling interventions based on time or reacting to failures, predictive maintenance uses real-time data from machines to determine the optimal maintenance moment.
This strategy relies on three core principles:
-
Continuous monitoring of machine condition
-
Detection of abnormal patterns or deviations
-
Prediction of future failures before they occur
With predictive maintenance, maintenance is performed only when necessary—neither too early nor too late.
How Predictive Maintenance Works
The implementation of predictive maintenance follows a structured data-processing pipeline.
1. Sensors Collect Machine Condition Data
Sensors attached to machines gather real-time information about:
-
Temperature
-
Vibration and acceleration patterns
-
Pressure
-
Speed and rotation
-
Electrical consumption
-
Acoustic signatures
These variables allow the system to identify deterioration long before it causes failure.
2. Data Is Transmitted to a Monitoring System
Collected data is sent to local servers or cloud platforms. Modern factories often use IIoT networks (Industrial Internet of Things) to transmit machine information securely and continuously.
3. Algorithms Analyze Patterns and Detect Anomalies
This is the core function of predictive maintenance. Machine-learning models analyze real-time and historical data to:
-
Identify deviations from normal operating behavior
-
Detect early signs of component fatigue
-
Recognize patterns that precede failures
-
Predict the remaining useful life (RUL) of parts
The analysis process transforms raw sensor data into actionable insights.
4. Maintenance Teams Receive Alerts Before Failure
Instead of discovering problems after a breakdown, technicians receive warnings at the earliest detectable stage.
Typical alerts include:
-
“Bearing wear progressing—service recommended within 48 hours”
-
“Vibration amplitude exceeding threshold—inspect spindle alignment”
-
“Temperature irregularities detected—possible lubrication issue”
Teams can then schedule maintenance during low-impact time windows.
5. Maintenance Occurs Only When Needed
This eliminates unnecessary interventions and prevents sudden downtime, creating an optimized balance between productivity and reliability.
Benefits of Predictive Maintenance
The benefits of predictive maintenance extend across efficiency, cost, and operational stability.
Reduced Downtime
Predictive systems identify issues early enough to prevent unplanned downtime.
Downtime reduction directly increases output and improves delivery reliability.
Lower Maintenance Costs
Maintenance is performed only when indicators show it is necessary:
-
Fewer unnecessary service operations
-
Reduced spare parts consumption
-
Decreased overtime and emergency repair costs
Extended Machine Lifespan
Early detection prevents secondary damage. Machines remain operational longer with more consistent performance.
Higher Safety and Quality
Defects often correlate with safety risks and quality deviations. Predictive maintenance:
-
Prevents hazardous conditions
-
Reduces scrap and quality failures
-
Improves process stability
Improved Planning and Resource Allocation
Maintenance supervisors can schedule interventions strategically at low-impact times, improving coordination between teams and production managers.
According to operations research published by McKinsey & Company, predictive maintenance programs can reduce downtime by up to 40% and maintenance costs by 10–20%.
These numbers illustrate the transformative potential of predictive maintenance in modern industry.
Challenges in Implementing Predictive Maintenance

While the benefits are clear, implementation poses challenges:
-
Need for robust sensor infrastructure
-
Integration with legacy machines in production
-
Complexity of setting up data pipelines
-
Requirement for technical expertise
-
Initial budget for hardware and software
Companies must invest time in cleaning data, training staff, and adjusting operational workflows.
Overcoming these barriers is essential for fully leveraging predictive maintenance.
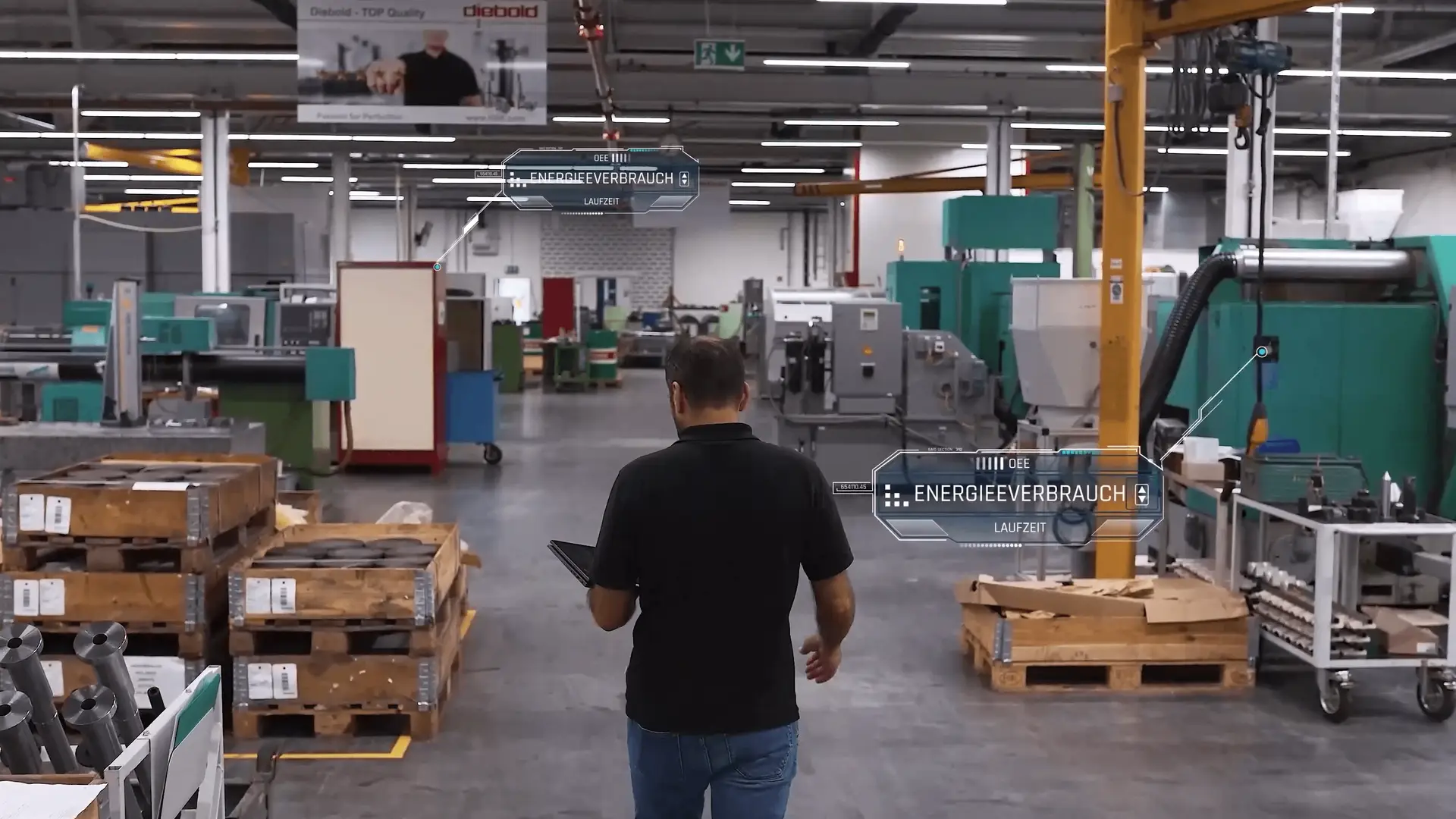

How Predictive Maintenance Transforms Production Strategy
Predictive maintenance shifts maintenance strategy from reactive firefighting to proactive planning. It transforms maintenance into a data-driven discipline, enabling:
-
Continuous production monitoring
-
Elimination of guesswork
-
Objective understanding of machine behavior
-
Alignment between maintenance and production goals
This evolution supports broader Industry 4.0 initiatives, enhances competitiveness, and enables manufacturing environments to operate with stability and precision.
Conclusion
Predictive maintenance changes the fundamental logic of production maintenance. Instead of relying on fixed schedules or reacting to breakdowns, factories can monitor machine conditions continuously and intervene only when necessary. This reduces downtime, cuts costs, improves quality, and extends machine lifespan.
As manufacturing becomes more automated and data-driven, predictive maintenance becomes a critical requirement—not an optional upgrade. The ability to anticipate failure and act at the optimal moment is now one of the defining advantages in modern production environments.