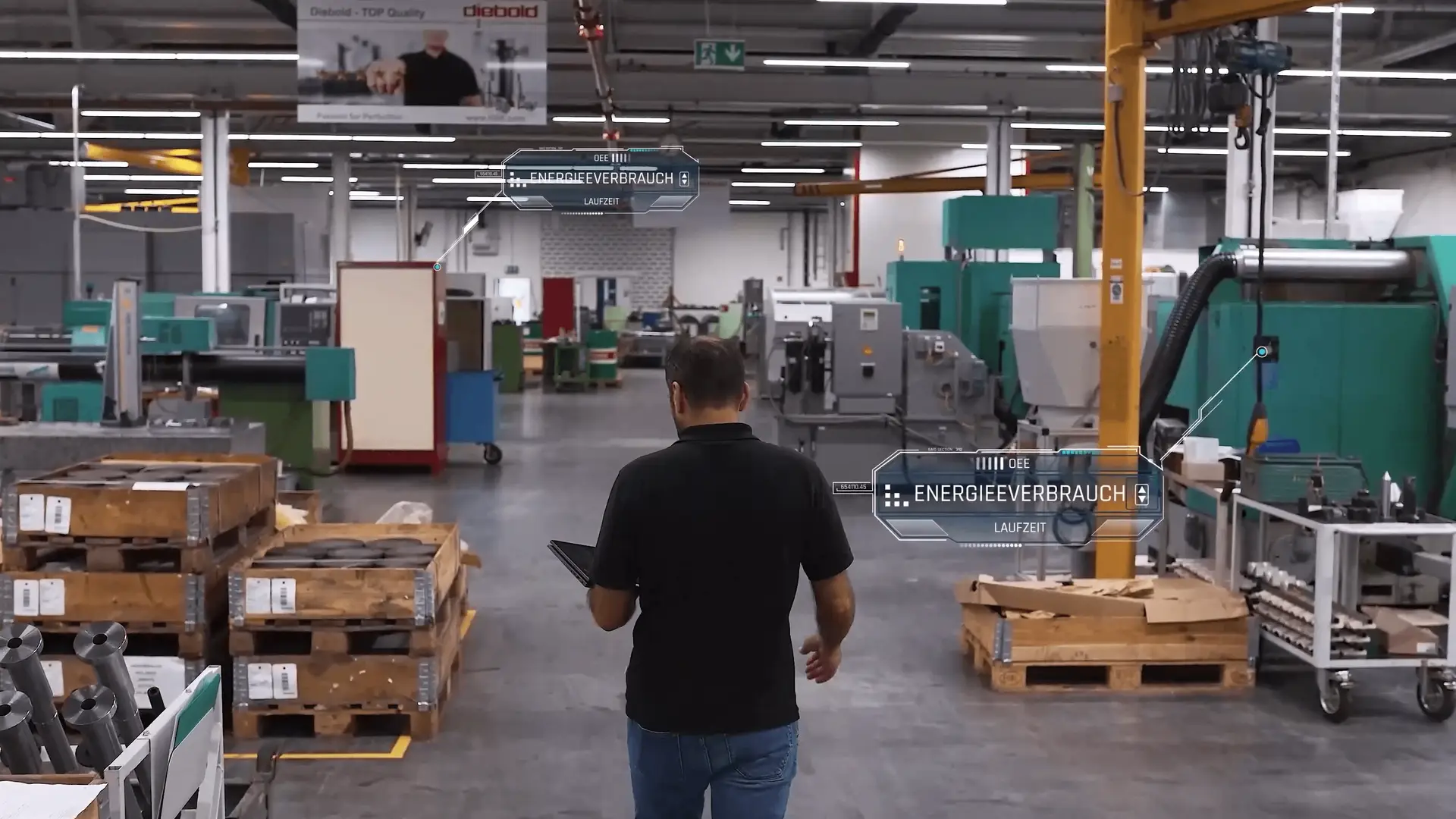
Machine Data Collection in Manufacturing: How Big Data Transforms Modern Production
Digital transformation in industrial environments is no longer optional. Today, machine data collection in manufacturing plays a central role in improving efficiency, increasing process transparency, predicting failures, minimizing waste, and enabling smart, automated decision-making. As factories deploy more sensors, machines, and connected systems, the volume of production data grows exponentially—and with it, the potential to fundamentally reshape how manufacturing operates.
Big Data has become one of the most powerful forces in industry. According to the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), modern manufacturing increasingly relies on high-quality, real-time data to improve accuracy, strengthen decision-making, and reduce operational variability.
This article explores how machine data collection in manufacturing drives precision, forecasting, traceability, customization, performance tracking, and operational efficiency. It also outlines how IIoT, automated systems, and analytics are transforming production lines and supply chains worldwide.
Why Machine Data Collection in Manufacturing Matters
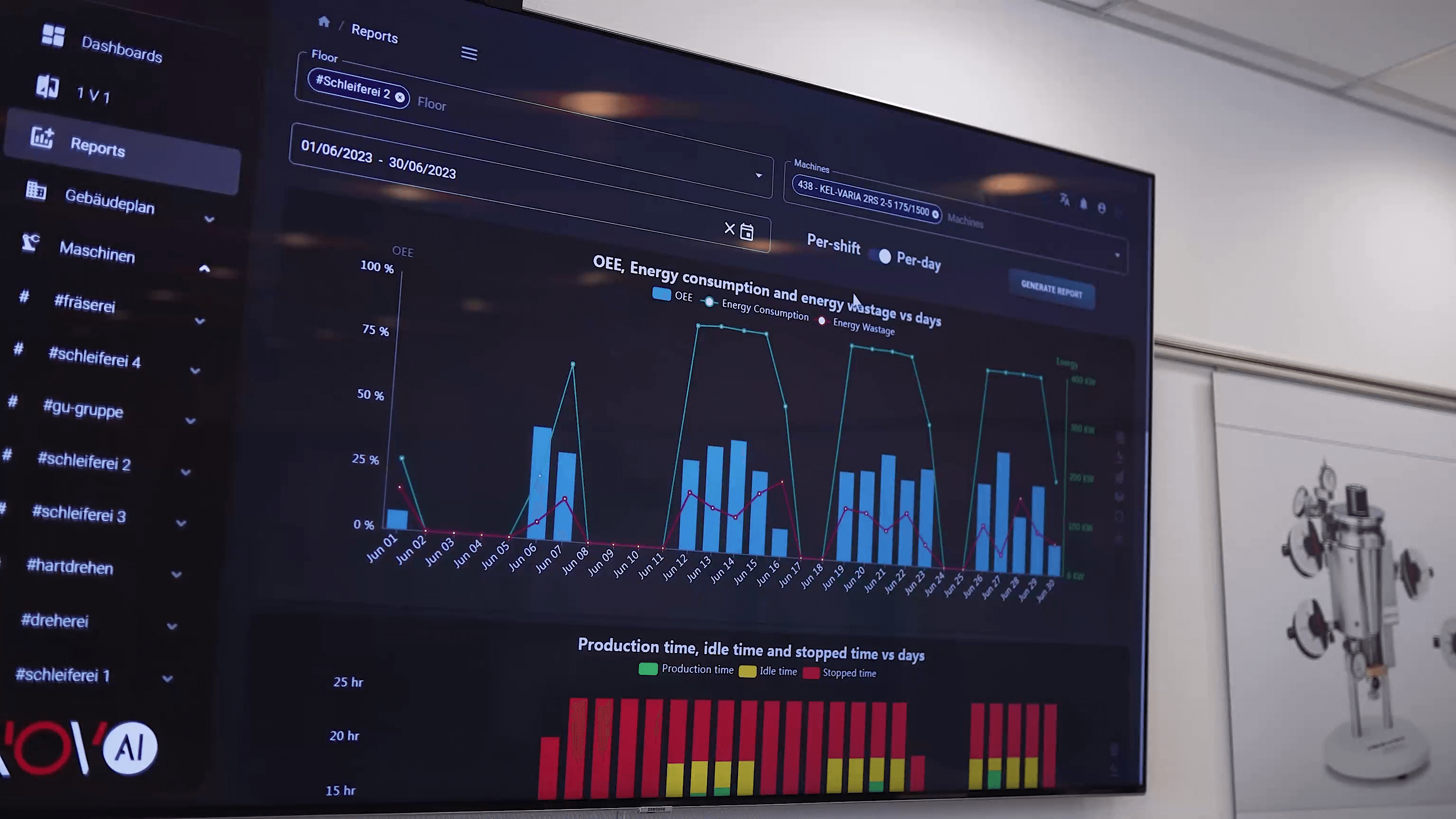
Every machine, sensor, and system on a production line produces data—temperature, vibration, torque, cycle counts, energy consumption, pressure, error logs, throughput rates, and much more. This raw data becomes meaningful only when properly captured, processed, and analyzed.
Machine data collection in manufacturing allows companies to:
-
uncover inefficiencies
-
detect anomalies earlier
-
forecast demand and supply chain fluctuations
-
improve product quality
-
reduce downtime
-
optimize raw material usage
-
boost overall productivity
Big Data is not just a technical concept. It is a strategic asset that fundamentally shifts how industrial companies think, plan, and execute production.
1. High Precision Through Data-Driven Production
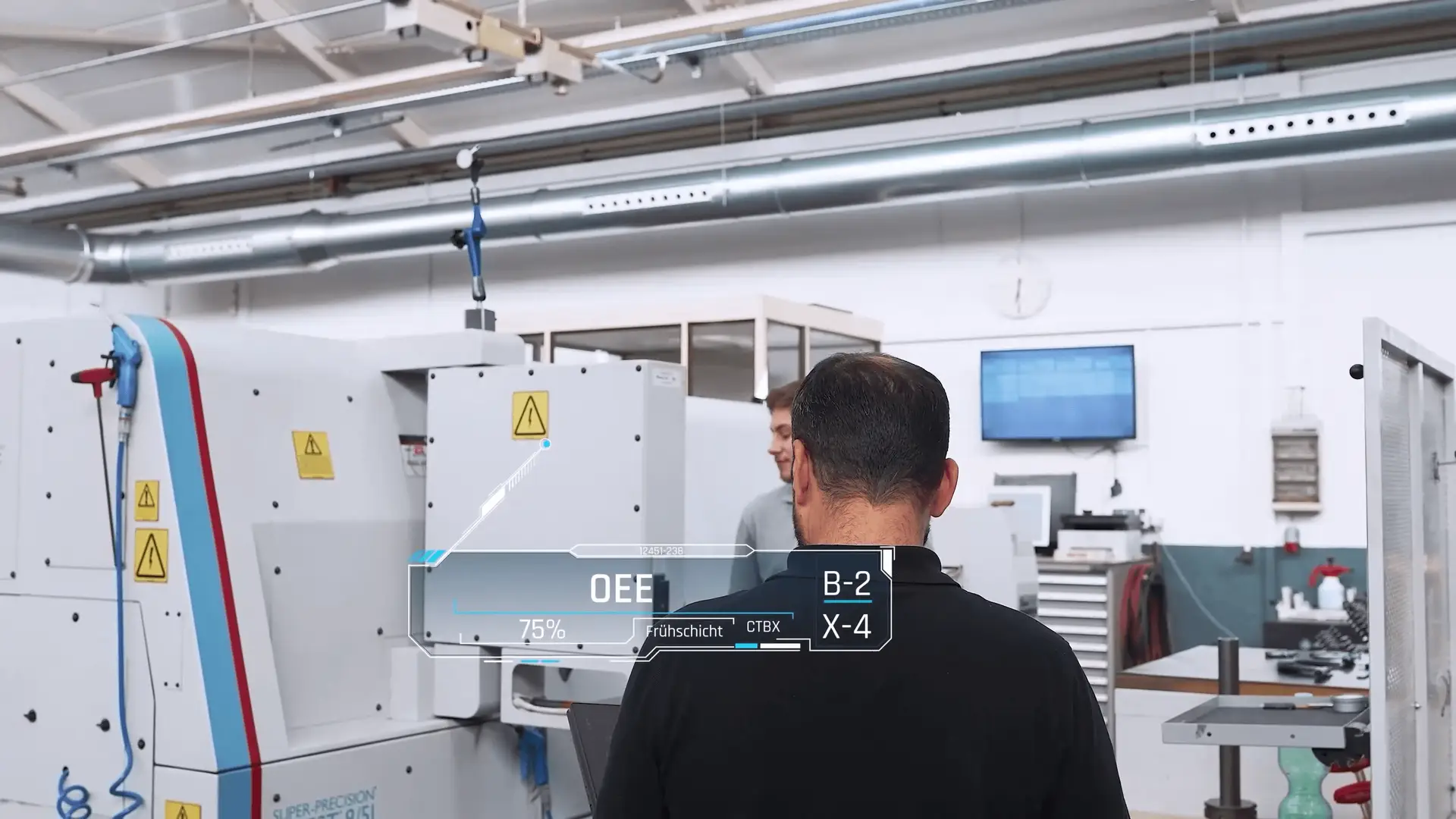

Before the era of analytics, companies relied heavily on machinery quality and operator expertise to maintain precision. Today, machine data collection in manufacturing enables producers to achieve accuracy levels previously impossible.
By collecting real-time sensor data, manufacturers can:
-
monitor microscopic process variations
-
identify deviations long before they impact final quality
-
optimize machine parameters continuously
-
reduce scrap and rework
-
identify the exact root cause of failures
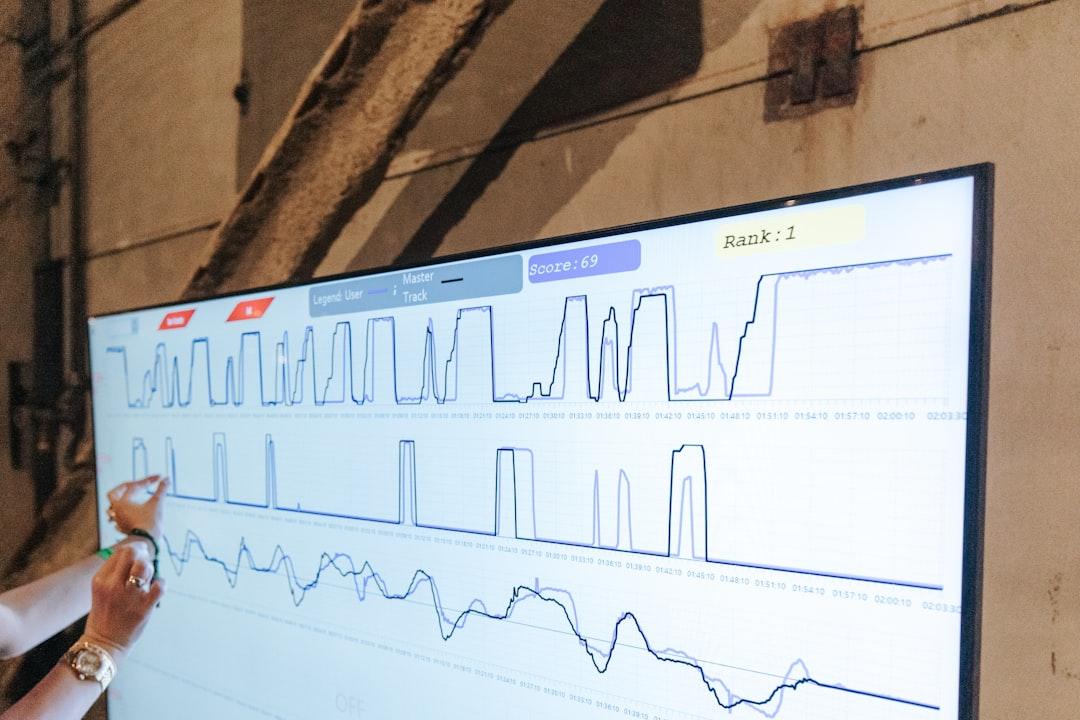
Machine data also supports advanced statistical process control (SPC) and real-time monitoring dashboards that help teams make immediate adjustments. This turns precision into a measurable, repeatable, and scalable advantage.

2. Better Predictions Across Supply Chains and Production Cycles
Forecasting is a critical element in modern manufacturing. However, traditional planning methods often fall short because they rely on historical averages rather than real-time information.
Machine data collection in manufacturing enables companies to:
-
forecast demand more accurately
-
adjust production schedules dynamically
-
manage inventory more efficiently
-
determine optimal production conditions
-
detect supply chain bottlenecks
Predictive models fueled by machine data help manufacturers understand how upstream and downstream changes influence production. This makes it easier to maintain balanced workloads, avoid stockouts, reduce excess inventory, and meet customer demand reliably.
3. Performance Tracking and Supplier Quality Evaluation
Machine data is not limited to production—it also plays a major role in evaluating supplier performance. When a supplier delivers parts or materials that impact machine performance or product quality, data helps quantify the issue immediately.
Machine data collection in manufacturing helps companies:
-
detect inferior materials
-
evaluate supplier performance based on measurable criteria
-
calculate long-term cost impact
-
compare the value of switching suppliers
-
assess whether to renegotiate terms or continue collaboration
Data-driven evaluations enable manufacturers to avoid subjective decisions and instead rely on measurable indicators of performance, quality, and reliability.
4. High Traceability Across the Manufacturing Lifecycle
In a world where transparency and product accountability are increasingly important, traceability has become essential. Machine data collection in manufacturing reveals exactly what happens at every stage of production.
Data can answer key questions:
-
How much raw material was consumed?
-
At which stage did inefficiency occur?
-
What was the performance of each batch?
-
How many units were produced per shift or per hour?
-
Which machines contributed to bottlenecks?
Traceability reduces waste, improves compliance, and strengthens quality control across the entire production chain.
For manufacturers facing regulatory requirements or customer audits, machine data becomes a central tool for demonstrating process reliability and product consistency.
5. Customization and Optimization Through Detailed Insights

The rise of customizable products places new demands on manufacturers. Machine data helps determine how processes should be adapted to support more flexible production.
Machine data collection in manufacturing enables:
-
improved raw material utilization
-
optimized process flows for short production runs
-
advanced customization based on real-world conditions
-
reverse engineering to refine existing processes
-
better configuration of machines for specialized batches
By analyzing machine behavior and adjusting parameters accordingly, manufacturers deliver customized products faster and at lower cost.
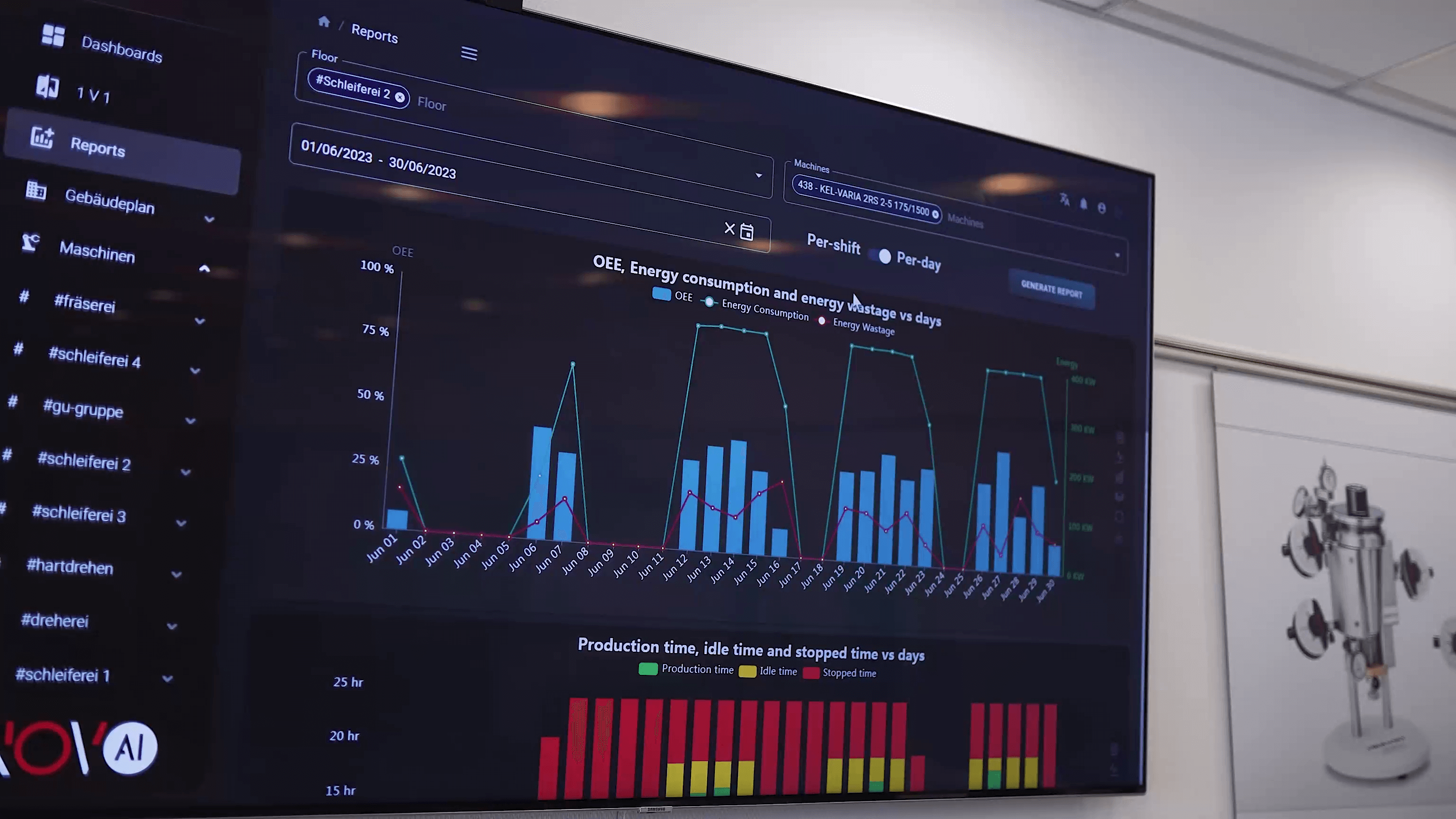
6. Improved Returns and Overall Operational Efficiency
Finally, machine data directly contributes to operational efficiency and ROI. By collecting machine data at scale, companies can evaluate the financial impact of new equipment, identify inefficiencies, and model operational changes.
Big Data analysis highlights:
-
how new machines influence productivity
-
whether advertising or promotions affect production demand
-
which processes generate the highest ROI
-
where energy consumption can be reduced
-
how workforce planning affects workflow
Analytics empowers decision-makers with insights that improve both short-term operations and long-term strategy.
IBM offers a useful overview of how Big Data analytics transforms industrial environments.
Two Main Directions for Modern Machine Data Collection in Manufacturing
1. Optimization of IIoT Production Lines
Manufacturers are deploying more sensors across their machines to capture detailed operational data, such as:
-
temperature
-
pressure
-
vibration
-
acoustics
-
humidity
-
energy consumption
-
cycle times
This data supports:
-
equipment diagnostics
-
energy analysis
-
quality incident investigation
-
real-time anomaly detection
-
predictive maintenance
-
root-cause analysis
Some advanced factories have adopted self-correcting automated systems. When processes deviate from standard conditions, alerts notify technicians instantly, enabling immediate correction and preventing the escalation of issues.
2. Optimization of the Supply Chain Through Data Integration
Machine data collection in manufacturing extends far beyond the factory floor. Supply chain optimization integrates:
-
logistics
-
distribution
-
warehousing
-
sales
-
customer behavior
-
supplier performance
-
internal enterprise systems
By aggregating all these data sources, companies can:
-
respond to customers faster
-
reduce operating costs
-
improve delivery accuracy
-
optimize transportation routes
-
balance supply and demand
-
streamline inventory management
Data connects the entire enterprise, from raw materials to final delivery.
Conclusion: Machine Data Collection in Manufacturing Is Reshaping the Industrial Landscape
Machine data collection in manufacturing is no longer a niche advantage—it is a core requirement for companies that want to thrive in a competitive global market. Through precision, forecasting, traceability, customization, performance tracking, and operational efficiency, machine data transforms how factories run, make decisions, and plan for the future.
The companies that invest in data collection and analytics gain:
-
lower downtime
-
higher quality output
-
more informed decisions
-
reduced operational costs
-
stronger competitive positioning
Machine data is the fuel that powers Industry 4.0—and the manufacturers who embrace it today will define the factories of tomorrow.