Machine Data in Production: Why Machine Data Drives Predictive Maintenance and Smarter Decisions
Modern manufacturing relies on one critical resource that is often underestimated: machine data in production. Every machine, sensor, and system in a production environment continuously generates information—raw, unstructured, and often overwhelming. Yet when properly collected, cleaned, and analyzed, this machine data becomes one of the most powerful assets for efficiency, competitiveness, and long-term performance.
According to the Oxford Dictionary, data consists of “raw facts and statistics collected together for reference or analysis.” In a production setting, these “raw facts” range from vibration signals and temperature fluctuations to cycle counts, torque values, error logs, and energy usage. Machine data in production is everywhere—but it only becomes valuable when processed, contextualized, and converted into actionable insights.
This article explores why machine data in production matters, how it supports predictive maintenance, how it reduces operational costs, and why it is essential for better decision-making. It also outlines the three most important use cases that show why industrial companies cannot afford to ignore machine data.
What Is Machine Data in Production?
Machine data in production refers to all measurable information generated by equipment during operation. This includes:
-
acoustic and vibration data
-
temperature and humidity values
-
optical and visual measurements
-
energy consumption and load fluctuations
-
pressure and flow data
-
error logs and machine states
-
cycle times and throughput
Because this data is raw, it requires pre-processing—the essential step where information is cleaned, filtered, and transformed into usable form. Pre-processing may include:
-
noise filtering
-
normalization
-
resampling
-
outlier removal
-
feature extraction
-
labeling
Correct preprocessing depends on understanding the machine and the nature of the signals. For example, filtering vibration noise requires knowing relevant frequency bands; preparing thermal data requires understanding expected temperature ranges. This makes domain knowledge a critical part of using machine data effectively.
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) confirms that high-quality manufacturing data is now a foundation for digital transformation and predictive analytics.
Machine data in production is the backbone of nearly all modern manufacturing improvements.
The Top Three Reasons Why Machine Data in Production Matters
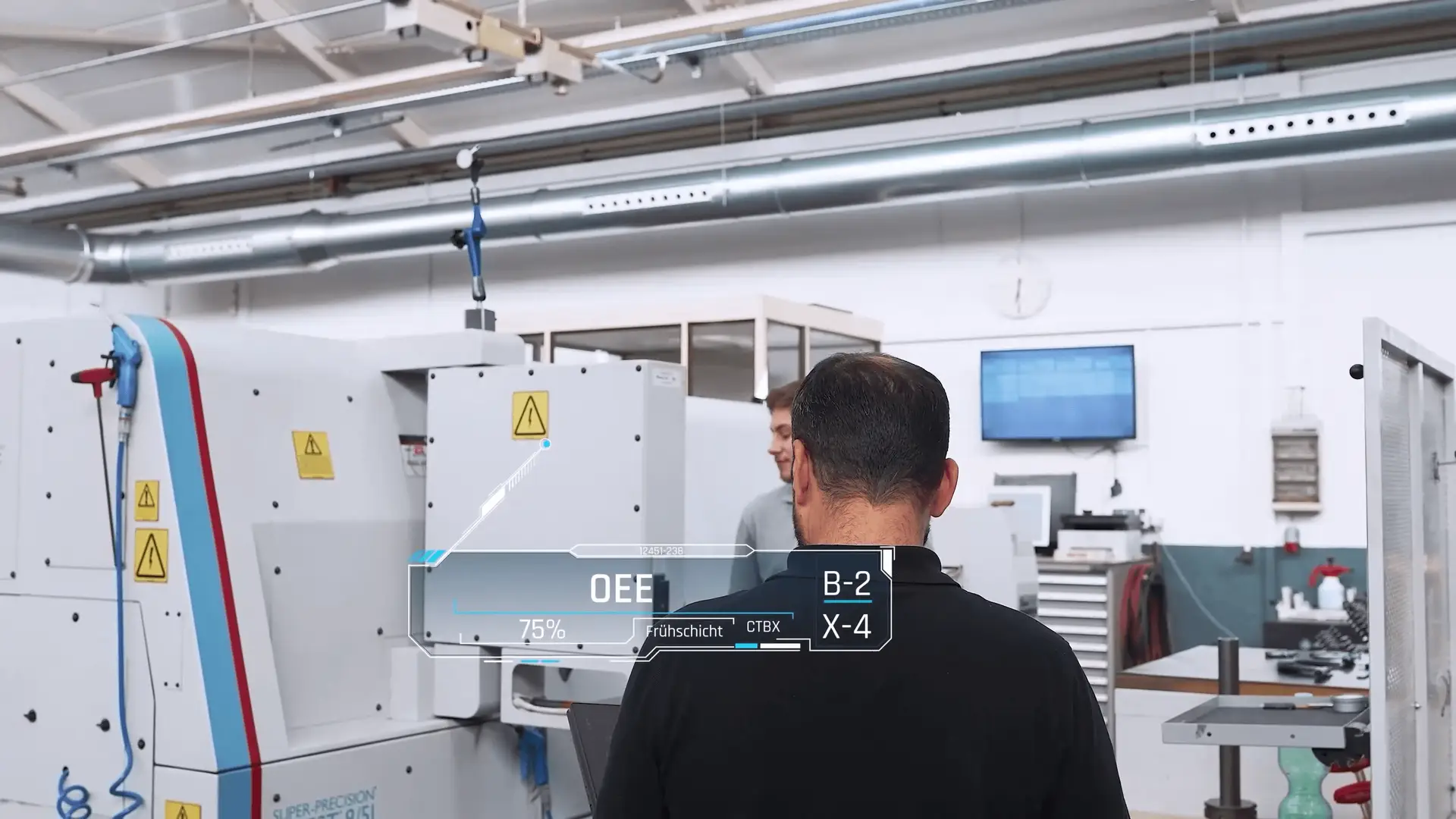
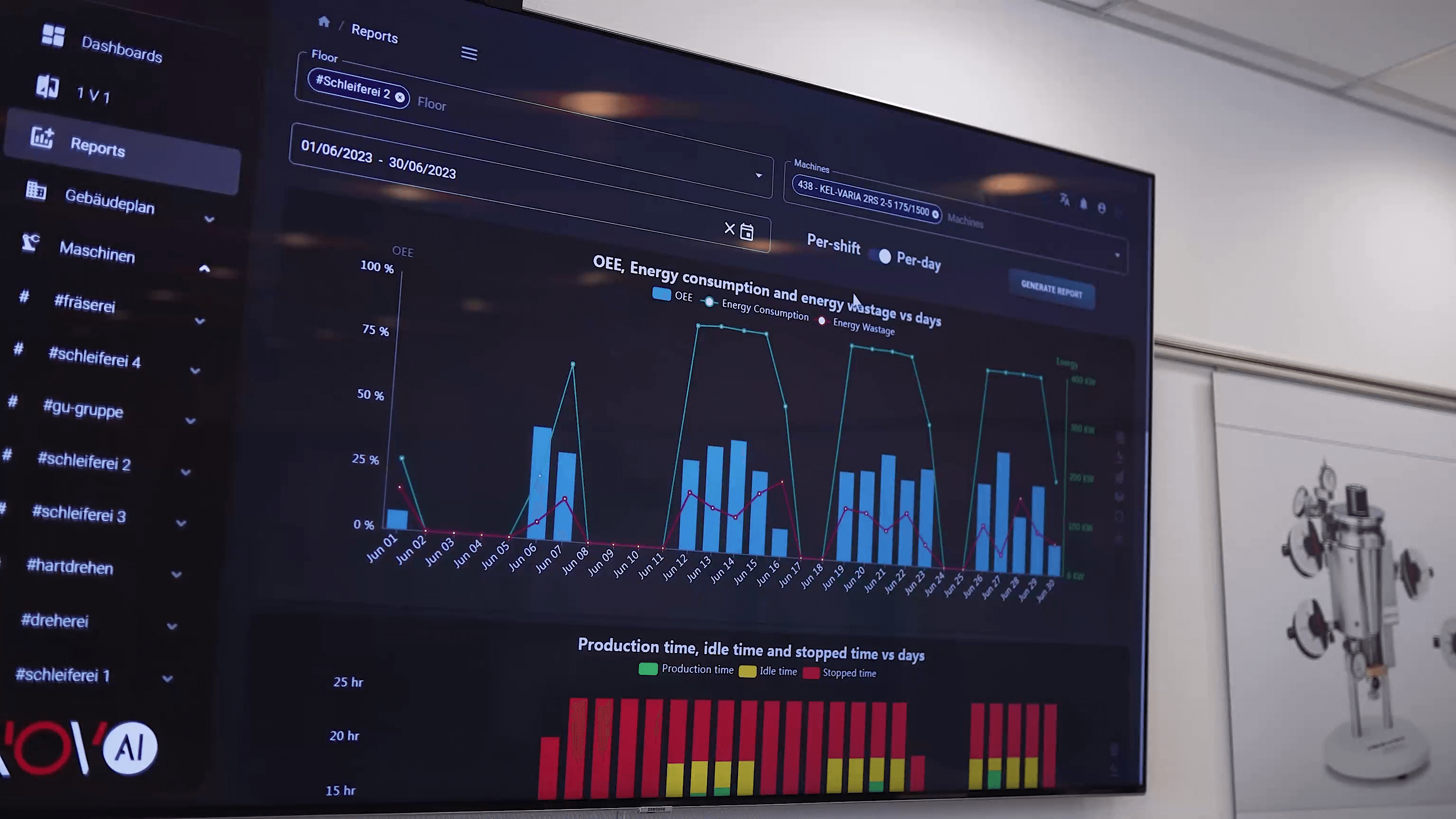
1. Predictive Maintenance and Failure Prevention
The primary value of machine data in production lies in its ability to support predictive maintenance. Maintenance teams need accurate, timely information to prevent failures—not just react to them.
Unplanned downtime disrupts production, increases costs, and can create safety and environmental risks. Machine data helps prevent this.
Predictive maintenance uses machine data to:
-
extend equipment lifetime
-
reduce catastrophic failures
-
maximize machine utilization
-
detect anomalies before they become severe
-
improve maintenance planning
One of the most powerful tools in predictive maintenance is anomaly detection, a method where machine-learning algorithms identify abnormal or unexpected patterns in machine signals. Unlike simple rule-based systems, anomaly detection can recognize early deterioration that humans often miss.
A real-world example comes from the airline industry. Southwest Airlines shares certain operational data with the National Weather Service, improving forecasts for conditions like icing or turbulence. According to Bloomberg, delays cause over $8 billion in losses in the airline sector. Predictive analytics helps reduce these delays by enabling crews and technicians to anticipate risks. As Tim Leonard, the airline’s director of flight ops compliance, notes:
"You can't take credit for the event that you avoid."
Predictive maintenance works the same way—its value lies in preventing what never becomes a problem.
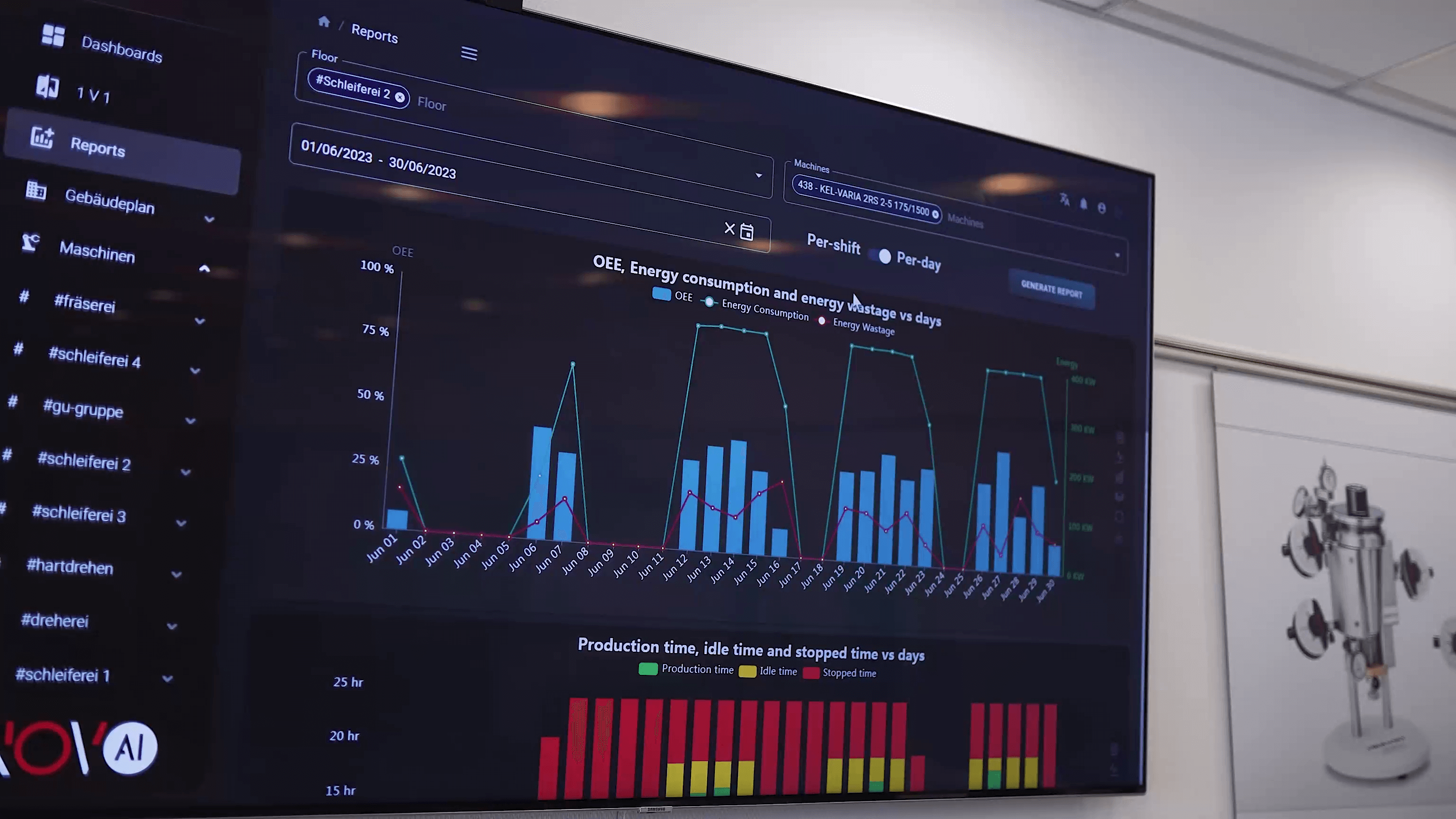
2. Cost Reduction and Process Efficiency
Machine data in production is essential not only for maintenance but also for cost optimization. Big data and modern analytics can dramatically change how production and supply chains operate.
Using machine data in production enables companies to:
-
reduce downtime costs
-
optimize energy usage
-
improve packaging and warehousing efficiency
-
reduce scrap and rework
-
optimize the cost of raw materials
-
lower transport and logistics expenses
Manufacturing companies that rely on machine data often experience significant financial benefits. For example, automotive manufacturers use analytics platforms to monitor steel prices and procurement timing. By maintaining databases of suppliers on distributed systems such as Hadoop, they track price fluctuations and select the best purchasing moment—reducing raw material costs.
Machine data also supports better understanding of customer behavior. Retailers use analytics to create targeted promotions, increase loyalty, and optimize inventory stocking based on demand patterns derived from machine and operational data.
Any company—whether in manufacturing, logistics, energy, or consumer goods—benefits from using machine data to identify bottlenecks, reduce waste, and improve capital allocation.
3. Better Decision-Making Through Data Transparency
Machine data in production improves how companies make decisions.
Accurate data enables:
-
better forecasting
-
more reliable planning
-
faster response to operational issues
-
improved product development
-
optimized resource allocation
-
more accurate risk assessment
Machine data supports strategic decisions because it reveals real performance instead of assumptions or estimates. It allows companies to identify patterns, evaluate trends, and understand long-term behavior.
A landmark study by MIT Sloan professors Andrew McAfee and Erik Brynjolfsson found that data-driven companies achieved 4% higher productivity and 6% higher profits than their competitors. Harvard Business Review explores this advantage in detail.
Machine data in production provides the truth behind operations—and truth is what drives better decisions.
Companies that treat machine data as a strategic asset make decisions with higher confidence and fewer risks.
Machine Data in Production Enables Industry-Wide Transformation
Recent research from LNS Research and MESA International found that machine data and analytics improve:
-
demand forecasting (46%)
-
plant performance understanding (45%)
-
customer service and support (39%)
Despite this, fewer than 20% of manufacturers use big data analytics effectively. Many executives still feel they are not leveraging machine data to its full potential.
This gap represents a major opportunity. Manufacturers that adopt machine-data strategies gain competitive advantages in:
-
responsiveness
-
process stability
-
cost management
-
quality control
-
innovation cycles
Machine data in production is not a luxury. It is now one of the essential building blocks of modern industrial competitiveness.
Conclusion: Machine Data in Production Is a Strategic Imperative
Machine data in production is more than numbers—it is the lifeblood of modern manufacturing. When collected, processed, and analyzed correctly, it enables predictive maintenance, reduces operational costs, and elevates decision-making across the organization.
Companies that use machine data effectively:
-
prevent failures
-
increase reliability
-
reduce waste
-
improve productivity
-
strengthen forecasting
-
gain competitive advantage
Companies that do not integrate machine data risk falling behind in an increasingly digital and competitive landscape.
Machine data has become indispensable. The organizations that embrace it will shape the next era of industrial performance and innovation.