Predictive Maintenance: Reducing Unplanned Downtime Through Data-Driven Maintenance Strategies
Unplanned downtime remains one of the most costly and disruptive events in industrial environments. It occurs when equipment unexpectedly stops functioning due to failures that have not been anticipated or detected in time. Unplanned downtime interrupts production, disrupts supply chains, damages customer relationships, and generates significant financial losses. A well-implemented predictive maintenance strategy directly targets these issues and enables companies to transition from reactive and scheduled maintenance to a data-driven approach that minimizes downtime and maximizes operational efficiency.
A ServiceMax survey revealed that the most frequent causes of unplanned downtime include hardware failures (46%), software issues (40%), and operator mistakes (17%). These disruptions can lead to cascading consequences across an entire production line. Manufacturing organizations incur high labor costs, emergency repair expenses, and lost production output. Deloitte estimates that ineffective maintenance strategies reduce overall productivity by 5% to 20%, demonstrating the critical importance of modernizing maintenance approaches.
Predictive maintenance addresses the core limitations of traditional maintenance models by analyzing the real-time condition of equipment and identifying developing failures before they materialize. Instead of following fixed intervals or waiting for breakdowns to occur, companies use predictive maintenance to make data-based decisions and schedule maintenance only when necessary.
The Shift From Traditional Maintenance to Predictive Maintenance
Conventional maintenance approaches fall into two categories: reactive and preventive. Reactive maintenance waits for equipment to fail before intervening. Preventive maintenance schedules service at predefined intervals, regardless of equipment condition. Both approaches are costly. Reactive maintenance results in operational chaos, while preventive maintenance often replaces components prematurely or interrupts production unnecessarily.
Predictive maintenance uses real-time equipment data, advanced analytics, and machine-learning models to monitor the health of machinery continuously. GE Oil & Gas found that predictive maintenance reduces average unplanned downtime to 5.24%. By comparison, planned maintenance results in 7.96% downtime and reactive maintenance in 8.43%. When fully implemented, predictive maintenance can reduce the financial impact of downtime by up to 60%.
Beyond uptime improvements, predictive maintenance significantly enhances safety and operational performance. Early detection of anomalies helps technicians plan maintenance activities before equipment reaches unsafe operating conditions. The reduction of emergency situations decreases risk exposure for employees and lowers insurance and compliance costs.
How Predictive Maintenance Works
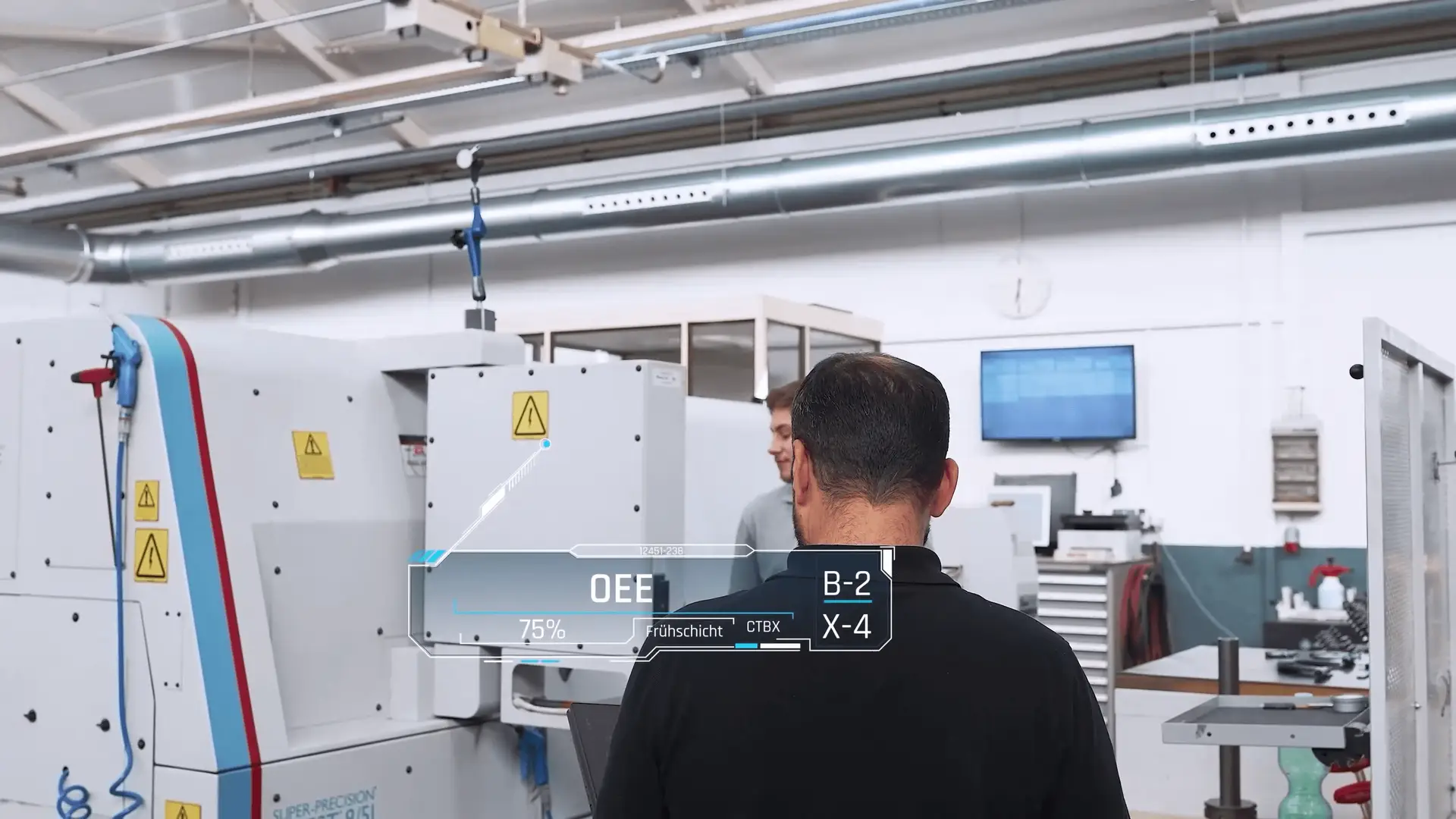

Predictive maintenance is a structured, technology-driven process that relies on several integrated components. The workflow consists of four primary steps: data acquisition, data transmission, data analysis, and actionable insights.
1. Data Acquisition Through Sensors
Predictive maintenance begins with continuous data collection from industrial machinery. Sensors monitor vibration patterns, acoustic signals, motor currents, temperatures, pressures, and energy consumption. These sensor inputs provide a real-time view of equipment condition. They detect subtle deviations that human operators cannot observe.
Modern IIoT sensors are compact, energy-efficient devices that attach directly to machines without requiring invasive modifications. The ability to retrofit sensors onto existing assets makes predictive maintenance accessible for companies that operate aging or heterogeneous machinery.
2. Data Transmission Through IT Infrastructure
Sensor data is transmitted either through local networks, industrial wireless systems, or secure cloud platforms. The underlying IT infrastructure must support reliable, low-latency communication and comply with industrial networking standards. Organizations increasingly align their data handling with international guidelines, such as those provided by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
Robust networking and cybersecurity protocols are essential to ensure that predictive maintenance systems are stable, safe, and scalable.
3. Data Processing and Analysis
Once data reaches a centralized platform, predictive models analyze the information to detect patterns indicative of wear, misalignment, lubrication issues, thermal stress, or other failure precursors. Algorithms evaluate both historical and real-time data, enabling continuous condition assessment.
This analytical layer determines:
-
emerging anomalies
-
performance degradation
-
remaining useful life of components
-
probability of failure
-
optimal timing for maintenance interventions
Predictive analytics enhance accuracy as machine learning models refine themselves using increasing volumes of operational data.
4. Actionable Insights and Automated Alerts
Predictive maintenance platforms visualize machine conditions through dashboards, trend graphs, and health indicators. When thresholds or patterns indicate potential risk, the system automatically sends alerts to maintenance teams. This early warning system provides time to plan repair activities, gather necessary tools or spare parts, and avoid unexpected shutdowns.
The U.S. Department of Energy reports that predictive maintenance can reduce maintenance costs by 25%–30% and cut downtime by 35%–45%. Additionally, organizations using predictive maintenance often see a tenfold increase in long-term return on investment.
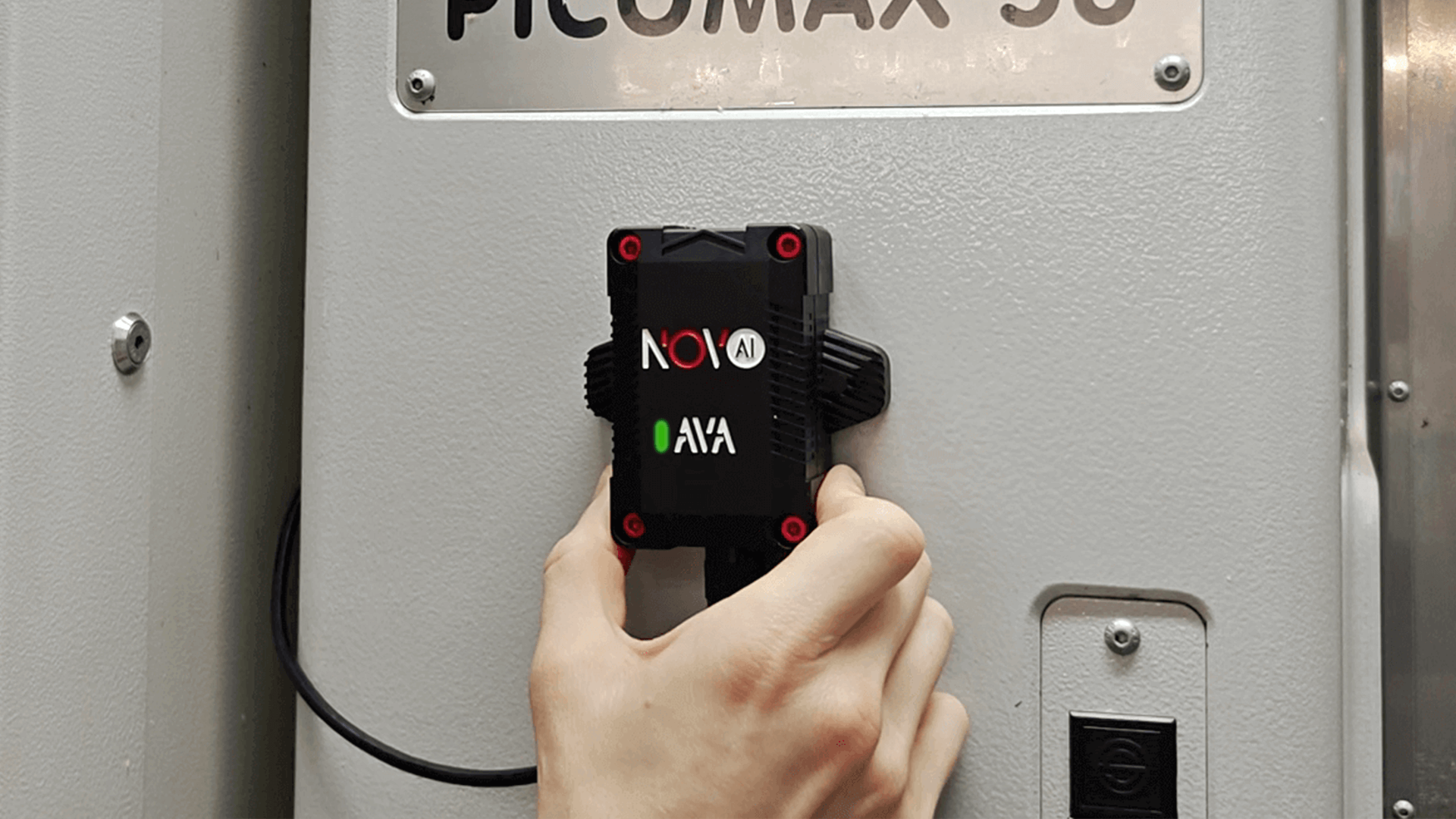

Requirements for Implementing Predictive Maintenance
A successful predictive maintenance program requires coherent planning and coordinated deployment of multiple technological and organizational components.
Sensor Infrastructure
Without high-quality sensors, predictive models cannot accurately assess machine conditions. Sensors must be calibrated, correctly positioned, and robust enough to withstand industrial environments.
IT and Networking Systems
Companies must ensure stable network coverage, secure data transmission, and integration with existing systems such as ERP, MES, and CMMS platforms. Compliance with standards set by organizations like the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) is essential for security and interoperability:
Data Management and Analytics
Organizations need cloud or on-premise analytics platforms capable of processing high-volume sensor data. Data scientists or trained engineers must configure and refine predictive algorithms.
Workforce Training
Personnel must understand how to interpret predictive maintenance insights and how to incorporate them into operational routines. Many small and medium-sized enterprises face a skills gap that must be addressed through training programs or external support.
Condition-Based Monitoring and Predictive Analytics
Predictive maintenance often operates in combination with condition-based monitoring. Condition-based monitoring focuses on observing current machine states, while predictive analytics extends this by forecasting future failures.
Novo AI provides a machine-monitoring solution that exemplifies this approach. The AVa IIoT sensor captures critical vibration, acoustic, and operational signals from machinery. The device identifies irregular patterns in machine components and transmits this data to the cloud through secure Wi-Fi connections.
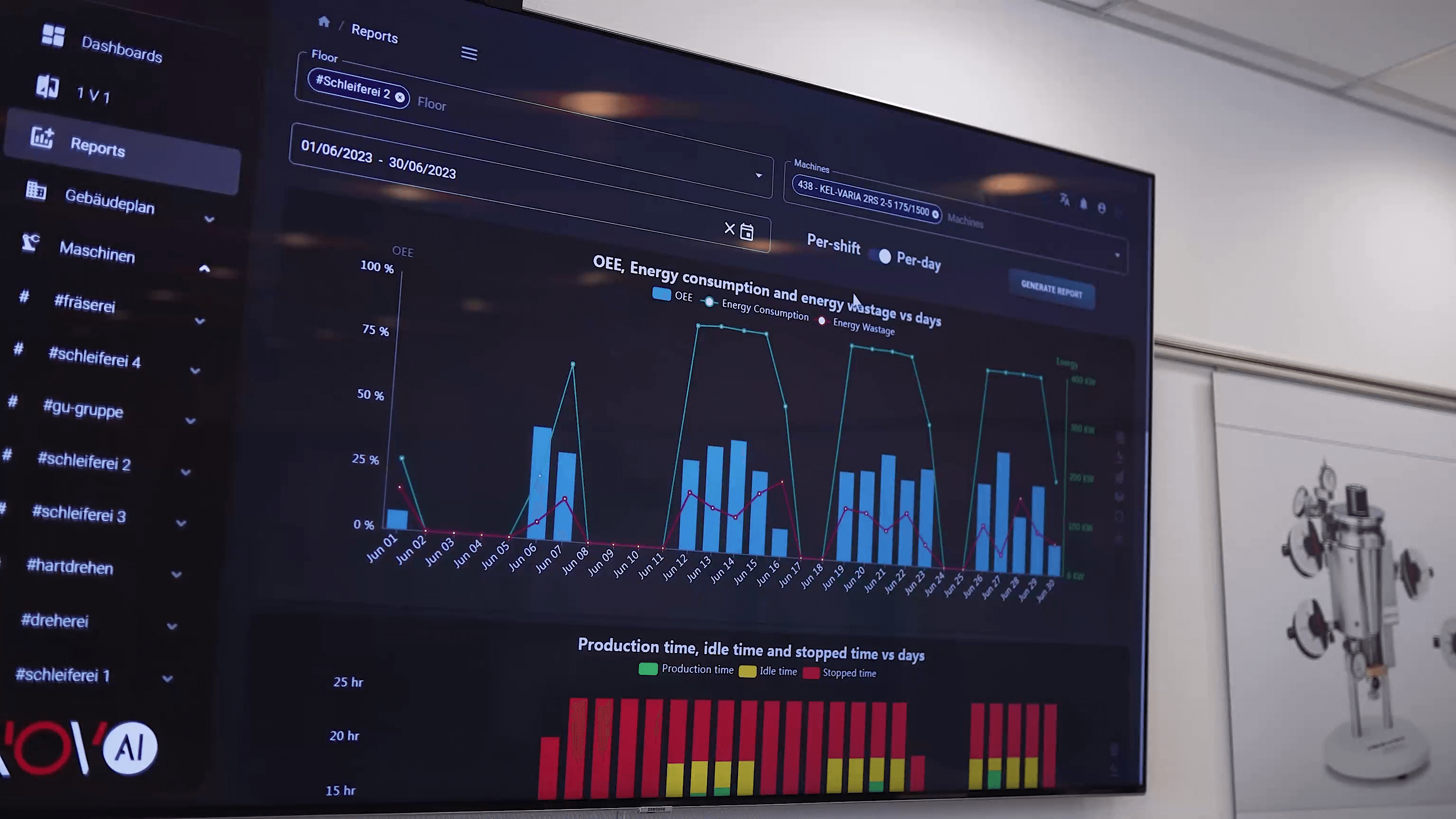
Once transmitted, the Watchmen platform processes and analyzes the data, transforming complex measurements into actionable insights. Users monitor machine health in real time through the Watchmen Dashboard, which provides a cockpit-style overview of operational conditions, anomaly detection, and performance trends. By integrating predictive maintenance with condition monitoring, companies obtain a comprehensive maintenance and production optimization solution.
The Future of Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance is evolving rapidly as AI models become more sophisticated, IIoT sensor hardware becomes more capable, and cloud platforms deliver greater computational power. Organizations that adopt predictive maintenance can expect increased asset longevity, improved energy efficiency, and enhanced production reliability.
Autonomous maintenance systems, AI-generated maintenance recommendations, and fully automated workflow integration will further reduce the need for manual oversight. Predictive maintenance is shifting from a competitive advantage to a foundational requirement for industry competitiveness.
Conclusion
Predictive maintenance transforms how industrial companies manage equipment reliability. By leveraging real-time sensor data, predictive analytics, and automated insights, organizations significantly reduce unplanned downtime and maintenance costs. Predictive maintenance enables efficient, safe, and streamlined operations, supporting long-term productivity and growth. As industrial environments continue to evolve, predictive maintenance stands as a central pillar of modern operational excellence.